What Part of the Brain Controls Blood Pressure Regulation
Pressure sensors located in the walls of your blood vessels detect changes in blood pressure and send messages to your brain directing it to make adjustments in your body that will affect your blood pressure ref 3. Its upper part is continuous with the pons.

Guide To The Human Brain Anatomy And Human Brain Functions Segregated By Lobes Brain Structure Inf Brain Anatomy And Function Brain Anatomy Human Brain Anatomy
It connects the brain to the spinal cord and controls automatic functions such as breathing digestion heart rate and blood pressure.

. It is controlled by the cardiovascular center in our brain and it forms a part of our autonomic nervous system. We may see it as a bridge of sorts. The hypothalamus helps control the pituitary gland and regulates many body functions.
The kidneys provide a hormonal mechanism for the regulation of blood pressure by managing blood volume. Higher brain regions such as the cerebral cortex hypothalamus and limbic system signal the cardiovascular center when conditions stress fightorflight response hot or cold temperature require adjustments to the blood pressure. The Rheos system see illustration works on baroreceptors.
The hypothalamus a small area of the brain involved in hormonal regulation produces corticotropin-releasing hormone and vasopressin. It connects the brain to the spinal cord and controls automatic functions such as breathing digestion heart rate and blood pressure. The hypothalamus helps control the pituitary gland and regulates many body functions.
The Limbic System Or Emotional Center. The list of structures that make up the limbic system are not agreed upon. How Your Brain Controls Blood Pressure.
At the bottom of the brainstem the medulla is where the brain meets the spinal cord. This is the quickest form of blood pressure regulation performed by our bodies. The device is designed to reduce blood pressure by using small electrical signals to influence the bodys blood pressure regulation system called the baroreflex.
These are located in the arch of the aorta and the carotid sinus. Functions of the medulla regulate many bodily activities including heart rhythm breathing blood flow and oxygen and carbon dioxide levels. The primary regulatory sites include the cardiovascular centers in the brain that control both cardiac and vascular functions.
The medulla contains the cardiac respiratory vomiting and vasomotor centers regulating heart rate breathing and blood pressure. For some people controlling blood pressure is a matter of eating a healthier diet exercising more and reducing stress. Apart from respiration these include the respiratory process as well as heart rate and blood pressure.
Others must add one or more medications. Regions of the limbic cortex. Herein what part of the brain controls blood pressure.
The cerebellum sits at the back of your head under the cerebrum. Helps in the transferring of messages between various parts of the brain and the spinal. Increased arterial pressure stretches the wall of the blood vessel triggering the baroreceptors.
Coordinates motor control signals sent between the brain and the body. Short-term regulation of blood pressure is controlled by the autonomic nervous system ANS. It controls coordination and balance.
Medulla oblongata Part of Hindbrain controls salivation and blood pressure. The brain stem regulates many important bodily processes all of which are automatic and without our conscious influence. The medulla oblongata myelencephalon is the lower half of the brainstem continuous with the spinal cord.
It controls coordination and balance. A portion of the hindbrain that controls autonomic functions such as breathing hear rate and digestion. The medulla is essential to survival.
The Rheos System is a pacemaker. Messages from the cortex to the spinal cord and nerves that branch from the spinal. Short-Term Regulation of Blood Pressure.
Four of the main regions of the limbic systems include. Stage 1 high blood pressure a diagnosis of hypertension is now between 130 and 139 systolic or between 80 and 89 diastolic the bottom number. Vasopressin and CRH trigger the pituitary gland to secrete corticotropin which stimulates the adrenal glands to produce corticosteroids.
Medulla The primary role of the medulla is regulating our involuntary life sustaining functions such as breathing swallowing and heart rate. UM Discovery Could Eventually Lead to Treatments. As part of the brain stem it also helps transfer neural messages to and from the brain and spinal cord.
Neurological regulation of blood pressure and flow depends on the cardiovascular centers located in the medulla oblongata. The cerebellum sits at the back of your head under the cerebrum. Answer 1 of 3.
The adrenal glands are controlled in part by the brain. Hypothalamic dysfunction is a problem with part of the brain called the hypothalamus. Respiration digestion heartbeat autonomic functions Part of the brainstem that controls vital life-sustaining functions such as heartbeat breathing blood pressure and digestion.
The brain stem sits beneath your cerebrum in front of your cerebellum. The brain stem sits beneath your cerebrum in front of your cerebellum. The medulla oblongata controls breathing blood pressure heart rhythms and swallowing.
Changes in blood pressure are detected by baroreceptors. January 1 2012. According to the newest guidelines a systolic blood pressure between 120 and 129 is known as elevated blood pressure.
Your body has complex mechanisms that help control your blood pressure which is is the force against your blood vessel walls ref 1. The cardiovascular center is located in the medulla oblongata of the brain stem and it provides a rapid neural mechanism for the. When these standard approaches dont do the trick a novel technique that uses a pacemaker-like device may someday help.
In adults normal blood pressure means you have readings below 12080.

Pin By Stephanie Daugherty On Chiari Syringomiela Chiari Neurological Disorders Nerve Damage

Brain Lobe Function Expressive Language Speech And Language Motor Cortex

Multiple System Atrophy Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia Brain Anatomy Somatosensory Cortex Brain Structure
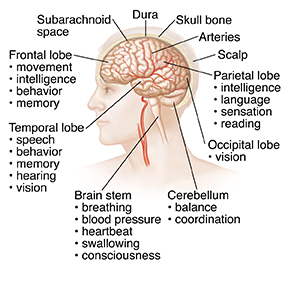
The Brain Saint Luke S Health System

Pin By Ela Elangovan On Neuroanatomy Diagrams Brain Diagram Anatomy Reference Brain Art

Pin By Mary Ann Horn On Justina Rumminger Occipital Lobe Brain Function Healthy Brain

Brain Areas Frontal Parietal Temporal Occipital Cerebellum Stem Brain Anatomy Psychology Medical Knowledge

Time Innerbrain Jpeg 576 333 Brain Lobes And Functions Brain Development Adolescent Health

Pin On Tbi Neurological Disorders And Their Effects

Pin On Meningioma Brain Tumor Awareness

Sign In Brain Anatomy Brain Anatomy And Function Brain Facts

Image Of The Major Parts Of The Brain And Their Functions Human Brain Facts Human Body Vocabulary Brain Facts

Pin On Brain Cancer Patient Resources

Dear Nurses The Brain Lobes Brain Lobes Nursing Mnemonics Nurse

Pin On Interoptex Daily Social

Different Functions Of The Brain Google Search Dr Caroline Leaf Occipital Lobe Brain Stem


Comments
Post a Comment